STF20NF06 Specs and Replacement
Type Designator: STF20NF06
Type of Transistor: MOSFET
Type of Control Channel: N-Channel
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Pd ⓘ - Maximum Power Dissipation: 28 W
|Vds|ⓘ - Maximum Drain-Source Voltage: 60 V
|Vgs|ⓘ - Maximum Gate-Source Voltage: 20 V
|Id| ⓘ - Maximum Drain Current: 20 A
Tj ⓘ - Maximum Junction Temperature: 175 °C
Electrical Characteristics
tr ⓘ - Rise Time: 15 nS
Cossⓘ - Output Capacitance: 100 pF
RDSonⓘ - Maximum Drain-Source On-State Resistance: 0.07 Ohm
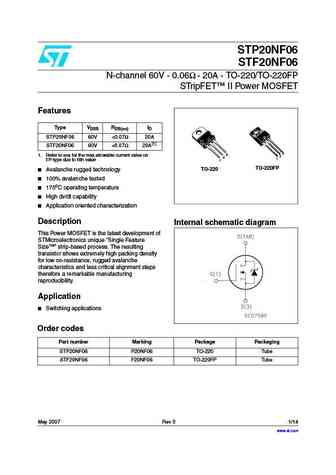
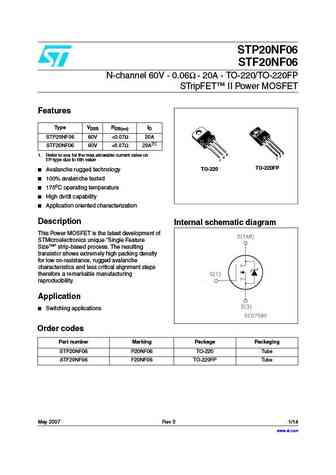
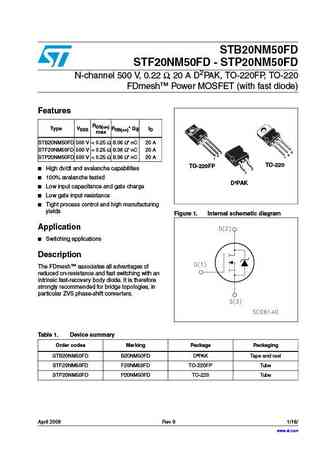
Package: TO-220FP
STF20NF06 substitution
- MOSFET ⓘ Cross-Reference Search
STF20NF06 datasheet
stp20nf06 stf20nf06.pdf
STP20NF06 STF20NF06 N-channel 60V - 0.06 - 20A - TO-220/TO-220FP STripFET II Power MOSFET Features Type VDSS RDS(on) ID STP20NF06 60V ... See More ⇒
stf20nf06.pdf
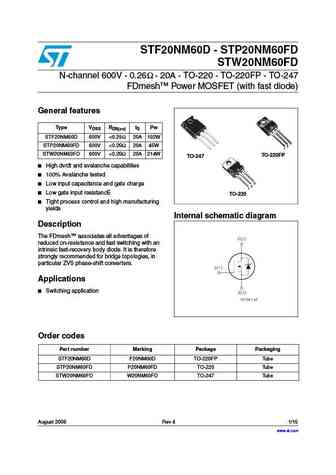
STP20NF06 STF20NF06 N-channel 60V - 0.06 - 20A - TO-220/TO-220FP STripFET II Power MOSFET Features Type VDSS RDS(on) ID STP20NF06 60V ... See More ⇒
stb20nf06l stf20nf06l stp20nf06l.pdf
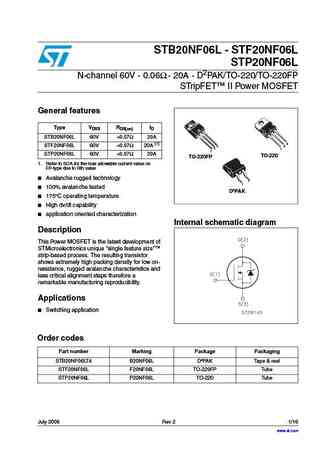
STB20NF06L - STF20NF06L STP20NF06L N-channel 60V - 0.06 - 20A - D2PAK/TO-220/TO-220FP STripFET II Power MOSFET General features Type VDSS RDS(on) ID STB20NF06L 60V ... See More ⇒
std20nf20 stf20nf20 stp20nf20.pdf
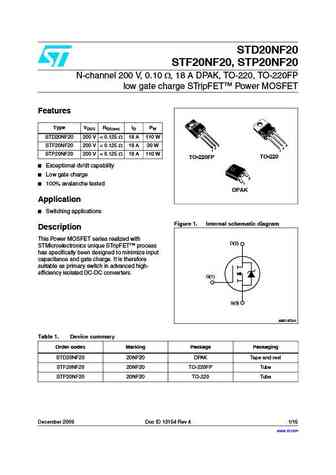
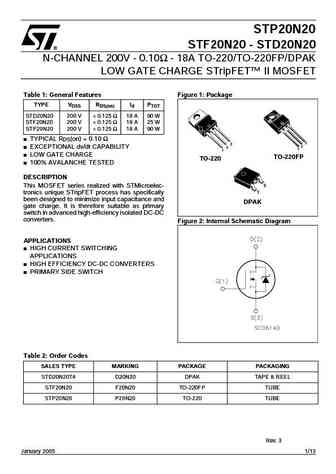
STD20NF20 STF20NF20, STP20NF20 N-channel 200 V, 0.10 , 18 A DPAK, TO-220, TO-220FP low gate charge STripFET Power MOSFET Features Type VDSS RDS(on) ID PW STD20NF20 200 V ... See More ⇒
Detailed specifications: STF16NM50N, STF18N60M2, STF18N65M2, STF18N65M5, STF18NM60ND, STF19NM65N, STF20N20, STF20N65M5, SI2302, STF21NM50N, STF21NM60N, STF23NM60N, STF24N60DM2, STF24N60M2, STF24N65M2, STF25N10F7, STF25N80K5
Keywords - STF20NF06 MOSFET specs
STF20NF06 cross reference
STF20NF06 equivalent finder
STF20NF06 pdf lookup
STF20NF06 substitution
STF20NF06 replacement
Can't find your MOSFET? Learn how to find a substitute transistor by analyzing voltage, current and package compatibility
History: SRC60R145B | NUS5531MT | JMSL1040AY | APM2314AC | TPM7002BKM | ZXMS6003G | DMC3032LSD
🌐 : EN ES РУ
LIST
Last Update
MOSFET: AUB062N08BG | AUB060N08AG | AUB056N10 | AUB056N08BGL | AUB050N085 | AUB050N055 | AUB045N12 | AUB045N10BT | AUB039N10 | AUB034N10
Popular searches
mje15030 transistor equivalent | 13003b | 2n6121 | 2sc1312 | bf495 transistor equivalent | 2sc1313 | 2sb560 replacement | 2sd330 replacement