NTB30N06L Specs and Replacement
Type Designator: NTB30N06L
Type of Transistor: MOSFET
Type of Control Channel: N-Channel
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Pd ⓘ - Maximum Power Dissipation: 88.2 W
|Vds|ⓘ - Maximum Drain-Source Voltage: 60 V
|Vgs|ⓘ - Maximum Gate-Source Voltage: 15 V
|Id| ⓘ - Maximum Drain Current: 30 A
Tj ⓘ - Maximum Junction Temperature: 175 °C
Electrical Characteristics
tr ⓘ - Rise Time: 200 nS
Cossⓘ - Output Capacitance: 260 pF
RDSonⓘ - Maximum Drain-Source On-State Resistance: 0.046 Ohm
Package: D2PAK
NTB30N06L substitution
- MOSFET ⓘ Cross-Reference Search
NTB30N06L datasheet
ntb30n06g ntp30n06 ntp30n06 ntb30n06.pdf
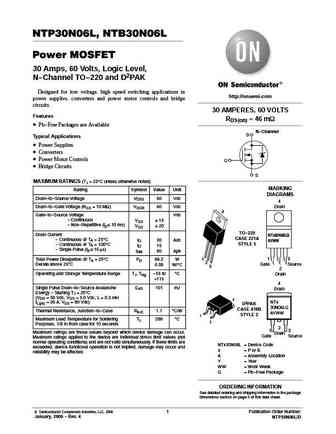
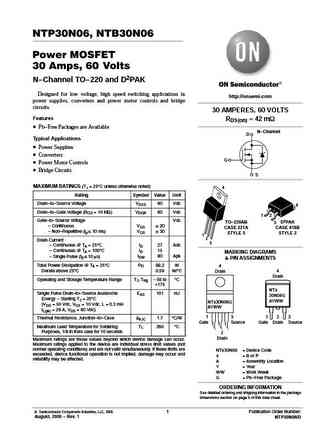
NTP30N06, NTB30N06 Power MOSFET 30 Amps, 60 Volts N-Channel TO-220 and D2PAK Designed for low voltage, high speed switching applications in http //onsemi.com power supplies, converters and power motor controls and bridge circuits. 30 AMPERES, 60 VOLTS Features RDS(on) = 42 mW Pb-Free Packages are Available N-Channel D Typical Applications Power Supplies Converters G... See More ⇒
ntb30n20.pdf
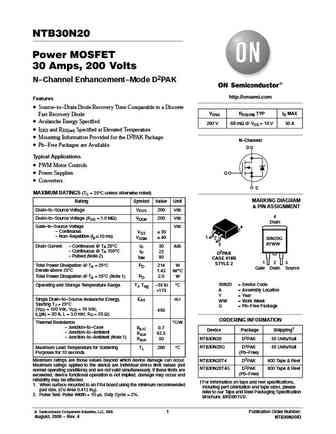
NTB30N20 Power MOSFET 30 Amps, 200 Volts N-Channel Enhancement-Mode D2PAK http //onsemi.com Features Source-to-Drain Diode Recovery Time Comparable to a Discrete VDSS RDS(ON) TYP ID MAX Fast Recovery Diode Avalanche Energy Specified 200 V 68 mW @ VGS = 10 V 30 A IDSS and RDS(on) Specified at Elevated Temperature Mounting Information Provided for the D2PAK Package N-... See More ⇒
Detailed specifications: NTB18N06, NTB18N06G, NTB18N06L, NTB23N03R, NTB23N03RG, NTB25P06G, NTB27N06LT4, NTB30N06G, 5N60, NTB30N20, NTB35N15G, NTB4302, NTB45N06G, NTB45N06LG, NTB52N10G, NTB5404NT4G, NTB5405NG
Keywords - NTB30N06L MOSFET specs
NTB30N06L cross reference
NTB30N06L equivalent finder
NTB30N06L pdf lookup
NTB30N06L substitution
NTB30N06L replacement
Learn how to find the right MOSFET substitute. A guide to cross-reference, check specs and replace MOSFETs in your circuits.
🌐 : EN ES РУ
LIST
Last Update
MOSFET: AUN084N10 | AUN065N10 | AUN063N10 | AUN062N08BG | AUN060N08AG | AUN053N10 | AUN050N08BGL | AUN045N085 | AUN042N055 | AUN036N10
Popular searches
a1015 transistor | c945 | ac128 transistor | 2n3055 transistor | 2n3904 datasheet | irf3710 | tip3055 | mosfet datasheet